Biomaterials
The improvement of a progressed biomaterial should go for controlling the time and spatial size of both the host response and the tissue repair process. These biomaterials should imitate at Nanoscale level the highlights of particular segments of the tissue extracellular lattice. Surface (covering as well as covalent connection of ligands to the surface of the polymers) or mass substance adjustments of broadly utilized manufactured or common biopolymers to limit the non-bio specific bond of proteins what's more, cells and to control the reaction of target cells (cell connection, relocation, multiplication, and separation). A few strategies utilized for miniaturized scale/nano designing of surfaces or multifunctional materials, for example, functionalized miniaturized scale/nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, nanowires have been proposed by the writing. Functionalized nanoparticles can be utilized for the conveyance of an assortment of distinctive mixes to tumors. Improvement of nanostructured biomaterials functionalized with novel focusing on and additionally effector areas or stacked with various medications may prompt generation of new great multifunctional nanodevices equipped for focusing on particular cells in tumor tissue and incite tumor relapse without causing lethality. The misuse of these systems is regularly upset by regular issues, for example, sterility, reproducibility, and cost of bioactive mixes when scaled to mechanical level.
Classification based on material source
1. Natural
Autograft – tissue transplanted from another part of the body pf the same individual Allograft – from a donor of the same species
Xenograft – from a donor of a different species Isograft – from
2. Synthetic – Metals, ceramics, polymers
Uses of Biomaterials
|
Uses of Biomaterials
|
Example
|
|
Replacement of diseased/damaged part
|
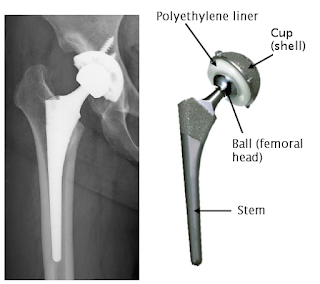
Artificial hip joint, kidney dialysis machine
|
|
Assist in healing
|
Sutures, bone plates, screws
|
|
Improve function
|
Cardiac pacemaker, intra-ocular lens
|
|
Correct functional abnormalities
|
Cardiac pacemaker
|
|
Correct cosmetic problem
|
Mastectomy augmentation, chin augmentation
|
|
Aid to diagnosis
|
Probes and catheters
|
|
Aid to treatment
|
Catheters drain
|
Materials for Use in the Body
|
Materials
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Examples
|
|
Polymers
nylon, silicon rubber, polyester, PTFE, etc
|
Resilient, easy to fabricate,
|
Not strong deforms with time, may degrade
|
Blood vessels, sutures, ear, nose, soft tissues
|
|
Metals
Ti and its alloys, Co-Cr alloys, stainless steels
|
Strong tough ductile
|
May corrode, dense, difficult to make
|
Joint replacement, bone plates and screws, dental root implant, pacer, suture
|
|
Ceramics
aluminum oxide, calcium phosphates including hydroxyapatite carbon
|
Very biocompatible, inert, strong in compression
|
Difficult to make, brittle, not resilient
|
Dental coating, orthopedic implants, femoral head of the hip
|
|
Composites
carbon-carbon, wire, fiber reinforced bone cement
|
Compression strong
|
Difficult to make
|
Joint implants, heart valves
|


Comments
Post a Comment